Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Stream
Stream là một chuỗi các sự kiện không đồng bộ đại diện cho nhiều giá trị sẽ đến trong tương lai. Lớp Stream xử lý các chuỗi sự kiện thay vì các sự kiện đơn lẻ. Stream có một hoặc nhiều trình lắng nghe (listener) và tất cả trình lắng nghe sẽ nhận được cùng một giá trị.
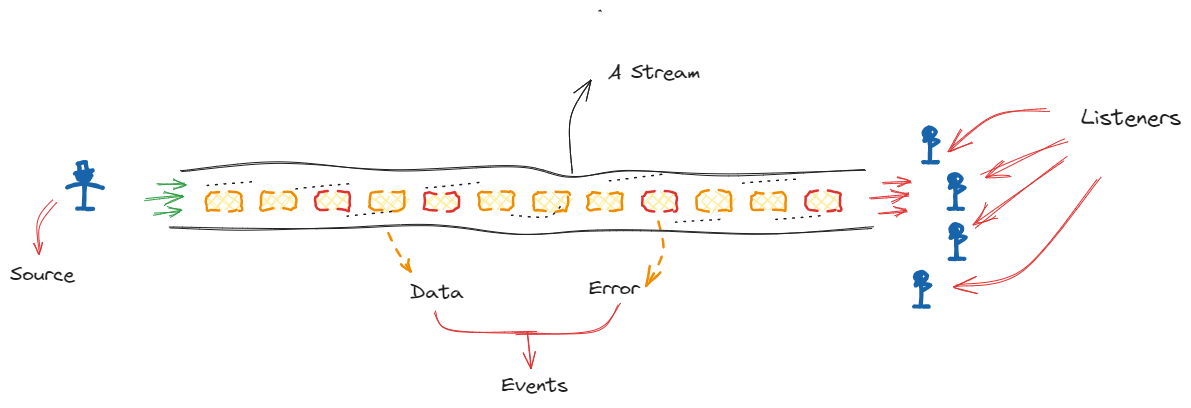
Một Stream giống như một đường ống phát ra các sự kiện, bạn đặt một phần tử lên một đầu đường ống và nó được chuyển tới cuối đường ống cho những bộ lắng nghe (listener). Mỗi phần tử trên Stream là một giá trị cụ thể hoặc một đối tượng Future vì vậy nó có thể hoàn thành với một giá trị hoặc trở thành một lỗi. Phần tử cũng có thể là một sự kiện "DONE" để báo hiệu sự kết thúc của Stream.
- | Single value | Zero or more values |
Sync | int | Iterator<int> |
Async | Future<int> | Stream<int> |
1. async* + yield
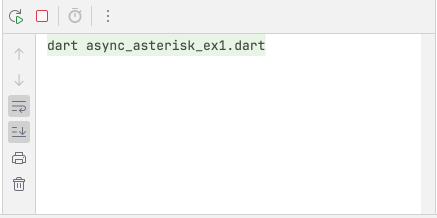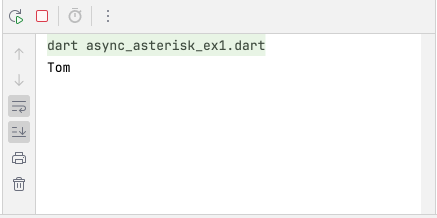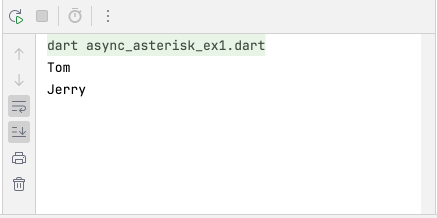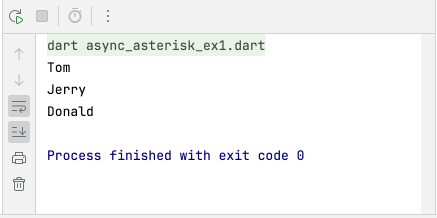
Đầu tiên, chúng ta hãy xem xét một ví dụ đơn giản. Phương thức getUserNames() cứ sau 2 giây lại trả về một tên người dùng.
async_asterisk_ex1.dart
Stream<String> getUserNames() async* {
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
yield 'Tom';
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
yield 'Jerry';
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
yield 'Donald';
}
Future<void> main() async {
await for (String name in getUserNames()) {
print(name);
}
}Chạy ví dụ trên bạn sẽ thấy các kết quả được in ra một cách ngắt quãng do thời điểm chúng tới là khác nhau.
| async vs async* Nói một cách ngắn gọn:
yield Từ khoá "yield" được sử dụng để phát ra (emit) một giá trị mà các bộ lắng nghe sẽ nhận được và nó không làm kết thúc hàm. |
| Từ khoá "return" không được sử dụng để trả về một giá trị trong các hàm async*, nhưng nó có thể được sử dụng để kết thúc hàm. Hàm async* cũng được là hàm Generator. |
2. sync* + yield
Trong khi từ khoá async* được sử dụng cho hàm không đồng bộ và trả về một Stream thì từ khoá sync* được sử dụng cho hàm đồng bộ và trả về một Iterable.
Từ khoá yield cũng được sử dụng trong hàm sync*, nó phát ra một giá trị và thêm vào Iterable.
sync_asterisk_ex1.dart
Iterable<String> getUserNames() sync* {
yield 'Tom';
yield 'Jerry';
yield 'Donald';
}
void main() {
for (String name in getUserNames()) {
print(name);
}
}
Output:
Tom
Jerry
Donald | sync* Nói một cách ngắn gọn:
yield Từ khoá "yield" trong hàm sync* được sử dụng để thêm một giá trị vào Iterable. |
| Từ khoá "return" không được sử dụng để trả về một giá trị trong các hàm sync*, nhưng nó có thể được sử dụng để kết thúc hàm. |
3. yield*
Từ khoá yield* được sử dụng bên trong một hàm async* để gọi tới một hàm async* khác để thêm các giá trị được phát ra bởi hàm đó vào hàm hiện tại.
async_yield_asterisk_ex1.dart
Stream<int> getStream(int n) async* {
if (n > 0) {
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
yield n;
yield* getStream(n - 1);
}
}
void main() {
getStream(3).forEach(print);
}Output:
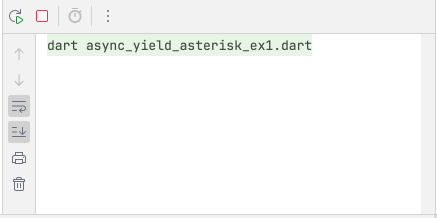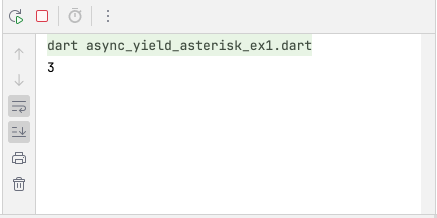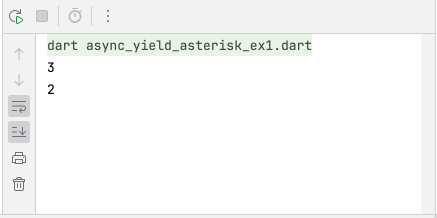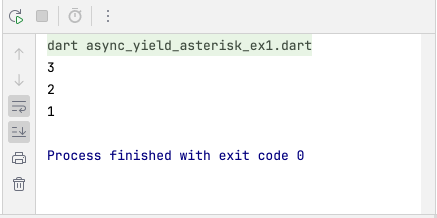
Từ khoá yield* cũng được sử dụng bên trong một hàm sync* để gọi tới một hàm sync* khác để thêm các giá trị được phát ra bởi hàm đó vào hàm hiện tại.
sync_yield_asterisk_ex1.dart
Iterable<int> getIterable(int n) sync* {
if (n > 0) {
yield n;
yield* getIterable(n - 1);
}
}
void main() {
getIterable(3).forEach(print);
}
Output:
3
2
1sync_yield_asterisk_ex2.dart
void main() {
final myIterable = getValues();
for (int value in myIterable) {
print(value);
}
}
Iterable<int> getValues() sync* {
yield 42;
yield* getThree();
yield* [6, 7, 8];
yield 24;
}
Iterable<int> getThree() sync* {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
}
Output:
42
1
2
3
6
7
8
244. Stream members
Các constructor của lớp Stream<T>:
const Stream();
const factory Stream.empty({bool broadcast});
factory Stream.value(T value);
factory Stream.error(Object error, [StackTrace? stackTrace]);
factory Stream.fromFuture(Future<T> future);
factory Stream.fromFutures(Iterable<Future<T>> futures);
factory Stream.fromIterable(Iterable<T> elements);
factory Stream.multi(void Function(MultiStreamController<T>) onListen,
{bool isBroadcast = false});
factory Stream.periodic(Duration period,
[T computation(int computationCount)?]);
factory Stream.eventTransformed(
Stream<dynamic> source, EventSink<dynamic> mapSink(EventSink<T> sink));Các thuộc tính:
Future<T> get first;
Future<T> get last;
Future<T> get single;
bool get isBroadcast;
Future<int> get length;
Future<bool> get isEmpty;Các phương thức:
static Stream<T> castFrom<S, T>(Stream<S> source);
Stream<T> asBroadcastStream(
{void onListen(StreamSubscription<T> subscription)?,
void onCancel(StreamSubscription<T> subscription)?});
StreamSubscription<T> listen(void onData(T event)?,
{Function? onError, void onDone()?, bool? cancelOnError});
Stream<T> where(bool test(T event));
Stream<S> map<S>(S convert(T event));
Stream<E> asyncMap<E>(FutureOr<E> convert(T event));
Stream<E> asyncExpand<E>(Stream<E>? convert(T event));
Stream<T> handleError(Function onError, {bool test(error)?})
Stream<S> expand<S>(Iterable<S> convert(T element));
Future pipe(StreamConsumer<T> streamConsumer);
Stream<S> transform<S>(StreamTransformer<T, S> streamTransformer);
Future<T> reduce(T combine(T previous, T element));
Future<S> fold<S>(S initialValue, S combine(S previous, T element));
Future<String> join([String separator = ""]);
Future<bool> contains(Object? needle);
Future<void> forEach(void action(T element));
Future<bool> every(bool test(T element));
Future<bool> any(bool test(T element));
Stream<R> cast<R>();
Future<List<T>> toList();
Future<Set<T>> toSet();
Future<E> drain<E>([E? futureValue]);
Stream<T> take(int count);
Stream<T> takeWhile(bool test(T element));
Stream<T> skip(int count);
Stream<T> skipWhile(bool test(T element));
Stream<T> distinct([bool equals(T previous, T next)?]);
Future<T> firstWhere(bool test(T element), {T orElse()?});
Future<T> lastWhere(bool test(T element), {T orElse()?});
Future<T> singleWhere(bool test(T element), {T orElse()?});
Future<T> elementAt(int index);
Stream<T> timeout(Duration timeLimit, {void onTimeout(EventSink<T> sink)?});Bên dưới là một vài ví dụ cho các constructor và phương thức thường dùng:
5. Stream.fromFutures()
Bạn cũng có thể tạo một Stream từ các Future(s) thông qua phương thức Stream.fromFutures().
stream_fromFutures_ex1.dart
import 'dart:math';
Future<int> getFutureIntValue() async {
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
int value = Random().nextInt(10);
return value;
}
Future<void> main() async {
Stream<int> stream = Stream.fromFutures([
getFutureIntValue(),
getFutureIntValue(),
getFutureIntValue(),
]);
await for (int value in stream) {
print("Value: $value");
}
}
Ví dụ sử dụng Stream.fromFutures() và yield*:
stream_fromFutures_ex2.dart
import 'dart:math';
Future<int> getFutureIntValue() async {
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
int value = Random().nextInt(10);
return value;
}
Stream<int> getValues() async* {
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
yield 10;
yield* Stream.fromFutures([
getFutureIntValue(),
getFutureIntValue(),
getFutureIntValue(),
]);
}
Future<void> main() async {
await for (int value in getValues()) {
print("Value: $value");
}
}
Output:
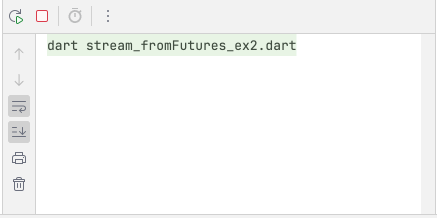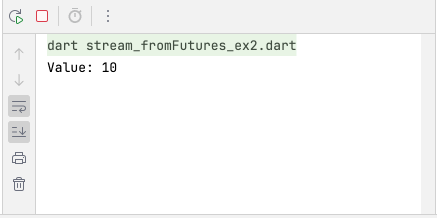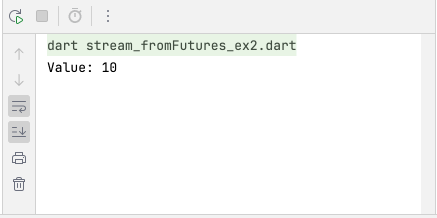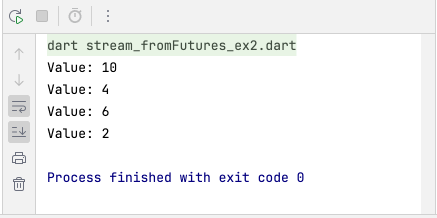
6. Stream.periodic()
Tạo ra một Stream phát ra các sự kiện một cách định kỳ.
- computationCount: 0, 1, 2,..
Stream.periodic()
factory Stream.periodic(Duration period,
[T computation(int computationCount)?]);Ví dụ:
stream_periodic_ex1.dart
void main() {
final stream = Stream<int>.periodic(
const Duration(seconds: 1),
(count) => count * count,
).take(5);
stream.forEach(print);
}
7. where()
Phương thức này trả về một Stream mới chỉ bao gồm các sự kiện phù hợp với hàm test() cho bởi tham số.
where()
Stream<T> where(bool test(T event));Ví dụ:
stream_where_ex1.dart
Future<void> main() async {
final stream = Stream<int>.fromIterable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]);
// Odd integers only
Stream<int> oddIntStream = stream.where((int event) => event % 2 == 1);
oddIntStream.forEach(print);
}Output:
1
3
5
78. reduce()
Future<T> reduce(T combine(T previous, T element));Ví dụ:
stream_reduce_ex1.dart
Future<void> main() async {
final stream = Stream<int>.fromIterable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]);
// Sum
Future<int> sumFuture = stream.reduce(
(int previous, int element) {
print("previous: $previous, element: $element");
return previous + element;
},
);
print("Final Result: ${await sumFuture}");
}
Output:
previous: 1, element: 2
previous: 3, element: 3
previous: 6, element: 4
previous: 10, element: 5
previous: 15, element: 6
previous: 21, element: 7
previous: 28, element: 8
Final Result: 36Các hướng dẫn lập trình Dart
- Kiểu dữ liệu Boolean trong Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ hàm trong Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Closures
- Interface trong Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ phương thức trong Dart
- Constructor trong Dart
- Property trong Dart
- Toán tử chấm chấm (..) trong Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Generics
- Lập trình Dart với công cụ trực tuyến DartPad
- Cài đặt Dart SDK trên Windows
- Cài đặt Visual Studio Code trên Windows
- Cài đặt Dart Code Extension cho Visual Studio Code
- Cài đặt Dart Plugin cho Android Studio
- Chạy ví dụ Dart đầu tiên của bạn trong Visual Studio Code
- Chạy ví dụ Dart đầu tiên của bạn trong Android Studio
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Stream
- Dart JSON với thư viện dart:convert
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart List
- Biến (Variable) trong ngôn ngữ Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Map
- Vòng lặp trong Dart
- Xử lý Dart JSON với gói dart_json_mapper
- Trình chuyển đổi mã nguồn (Transpiler) là gì?
- Phân tích XML trong Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart http
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Future
- Các phương thức mở rộng (Extension) trong Dart
- Mixins trong Dart
- Bài thực hành Dart phân tích JSON với gói dart:convert
- Bài thực hành Dart http CRUD
- Từ khoá part và part of trong Dart
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Dart Dio
- So sánh đối tượng trong Dart với thư viện Equatable
- Xử lý lỗi trong Dart Stream
- Dart Stream Single và Broadcast
Show More
