Kết nối cơ sở dữ liệu MySQL trong Python sử dụng PyMySQL
1. PyMySQL là gì?
Để kết nối từ Python vào một cơ sở dữ liệu bạn cần một Driver (bộ điều khiển), nó là một thư viện dùng để nói chuyện với cơ sở dữ liệu. Với cơ sở dữ liệu MySQL bạn có 3 sự lựa chọn Driver như vậy:
- MySQL/connector for Python
- MySQLdb
- PyMySQL
Driver | Mô tả |
MySQL/Connector for Python | Đây là một thư viện được cung cấp bởi chính cộng đồng MySQL. |
MySQLdb | MySQLdb là thư viện giúp kết nối vào MySQL từ Python, nó được viết trên ngôn ngữ C, nó được cung cấp miễn phí và là mã nguồn mở. |
PyMySQL | Đây là một thư viện giúp kết nối vào MySQL từ Python, là một thư viện thuần Python. Mục tiêu của PyMySQL là thay thế cho MySQLdb và làm việc trên CPython, PyPy và IronPython. |
PyMySQL là một dự án mã nguồn mở, và mã nguồn của nó bạn có thể xem tại đây:
2. Cài đặt PyMySQL
Để cài đặt PyMySQL trên Windows (Hoặc Ubuntu/Linux) bạn cần mở cửa sổ CMD, và thực thi lệnh sau:
pip install PyMySQL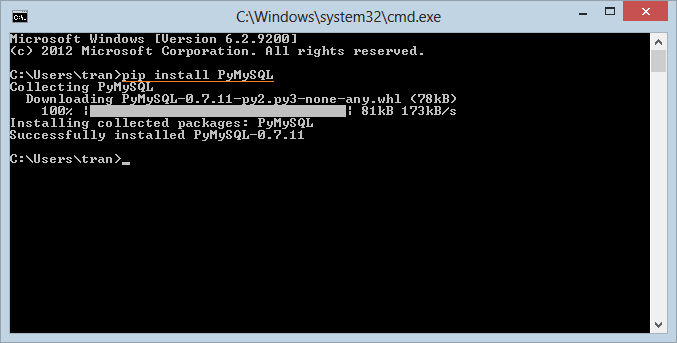
3. Database mẫu
"simplehr" là một cơ sở dữ liệu mẫu, được sử dụng trong nhiều hướng dẫn trên o7planning. Trong bài viết này tôi cũng sử dụng nó. Bạn có thể tạo cơ sở dữ liệu này theo hướng dẫn dưới đây:
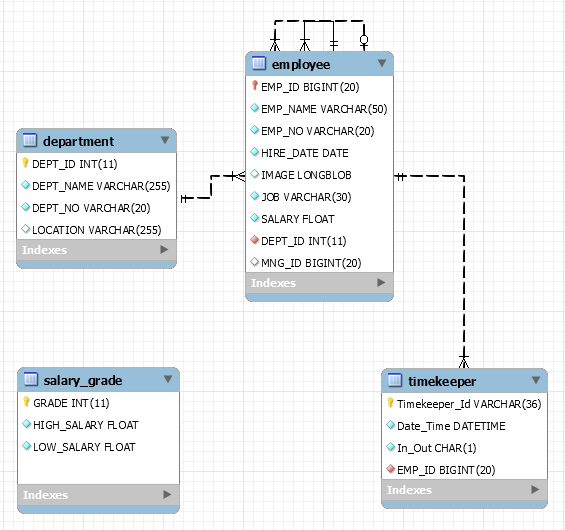
4. Kết nối MySQL từ Python với PyMySQL
Ví dụ đơn giản sau sử dụng Python kết nối vào MySQL và truy vấn bảng Department:
connectExample.py
import pymysql.cursors
# Kết nối vào database.
connection = pymysql.connect(host='192.168.5.134',
user='root',
password='1234',
db='simplehr',
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
print ("connect successful!!")
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# SQL
sql = "SELECT Dept_No, Dept_Name FROM Department "
# Thực thi câu lệnh truy vấn (Execute Query).
cursor.execute(sql)
print ("cursor.description: ", cursor.description)
print()
for row in cursor:
print(row)
finally:
# Đóng kết nối (Close connection).
connection.close()Kết quả chạy ví dụ:
connect successful!!
cursor.description: (('Dept_No', 253, None, 80, 80, 0, False), ('Dept_Name', 253, None, 1020, 1020, 0, False))
{'Dept_No': 'D10', 'Dept_Name': 'ACCOUNTING'}
{'Dept_No': 'D20', 'Dept_Name': 'RESEARCH'}
{'Dept_No': 'D30', 'Dept_Name': 'SALES'}
{'Dept_No': 'D40', 'Dept_Name': 'OPERATIONS'}Module tiện ích:
Một lời khuyên là bạn nên tạo ra một module tiện ích để tạo một kết nối tới cơ sở dữ liệu. Ở đây tôi tạo một module có tên "myconnutils", module này định nghĩa hàm getConnection() trả về một connection.
myconnutils.py
import pymysql.cursors
# Hàm trả về một connection.
def getConnection():
# Bạn có thể thay đổi các thông số kết nối.
connection = pymysql.connect(host='192.168.5.129',
user='root',
password='1234',
db='simplehr',
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
return connection5. Ví dụ Query
Ví dụ sau đây truy vấn bảng Employee, Python sử dụng %s như là một "nơi giữ chỗ" (placeholder) cho các tham số, nó không phụ thuộc kiểu của tham số. Ví dụ:
sql1 = "Insert into Department (Dept_Id, Dept_No, Dept_Name) values (%s, %s, %s) "
sql2 = "Select * from Employee Where Dept_Id = %s "queryExample.py
# Sử dụng module tiện ích của bạn.
import myconnutils
connection = myconnutils.getConnection()
print ("Connect successful!")
sql = "Select Emp_No, Emp_Name, Hire_Date from Employee Where Dept_Id = %s "
try :
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Thực thi sql và truyền 1 tham số.
cursor.execute(sql, ( 10 ) )
print ("cursor.description: ", cursor.description)
print()
for row in cursor:
print (" ----------- ")
print("Row: ", row)
print ("Emp_No: ", row["Emp_No"])
print ("Emp_Name: ", row["Emp_Name"])
print ("Hire_Date: ", row["Hire_Date"] , type(row["Hire_Date"]) )
finally:
# Đóng kết nối
connection.close()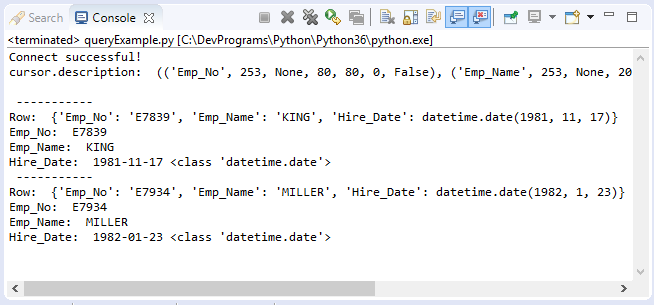
6. Ví dụ Insert
insertExample.py
# Sử dụng module tiện ích của bạn.
import myconnutils
import pymysql.cursors
connection = myconnutils.getConnection()
print ("Connect successful!")
try :
cursor = connection.cursor()
sql = "Select max(Grade) as Max_Grade from Salary_Grade "
cursor.execute(sql)
# 1 dòng dữ liệu
oneRow = cursor.fetchone()
# Output: {'Max_Grade': 4} or {'Max_Grade': None}
print ("Row Result: ", oneRow)
grade = 1
if oneRow != None and oneRow["Max_Grade"] != None:
grade = oneRow["Max_Grade"] + 1
cursor = connection.cursor()
sql = "Insert into Salary_Grade (Grade, High_Salary, Low_Salary) " \
+ " values (%s, %s, %s) "
print ("Insert Grade: ", grade)
# Thực thi sql và truyền 3 tham số
cursor.execute(sql, (grade, 2000, 1000 ) )
connection.commit()
finally:
connection.close()Output:
connect successful!!
Row Result: {'Max_Grade': 2}
Insert Grade: 37. Ví dụ Update
updateExample.py
# Sử dụng module tiện ích của bạn.
import myconnutils
import pymysql.cursors
import datetime
connection = myconnutils.getConnection()
print ("Connect successful!")
try :
cursor = connection.cursor()
sql = "Update Employee set Salary = %s, Hire_Date = %s where Emp_Id = %s "
# Hire_Date
newHireDate = datetime.date(2002, 10, 11)
# Thực thi sql và truyền 3 tham số.
rowCount = cursor.execute(sql, (850, newHireDate, 7369 ) )
connection.commit()
print ("Updated! ", rowCount, " rows")
finally:
# Đóng kết nối
connection.close()Output:
connect successful!
Update! 1 rows8. Ví dụ Delete
deleteExample.py
# Sử dụng module tiện ích của bạn.
import myconnutils
connection = myconnutils.getConnection()
print ("Connect successful!")
try :
cursor = connection.cursor()
sql = "Delete from Salary_Grade where Grade = %s"
# Thực thi sql và truyền 1 tham số
rowCount = cursor.execute(sql, ( 3 ) )
connection.commit()
print ("Deleted! ", rowCount, " rows")
finally:
# Đóng kết nối
connection.close()Output:
connect successful!
Deleted! 1 rows9. Gọi Thủ tục
Có một vài vấn đề khi bạn gọi một hàm (function) hoặc một thủ tục (procedure) trong Python. Tôi đặt ra môt tình huống như sau:
Bạn có một thủ tục:
- Get_Employee_Info(p_Emp_Id, v_Emp_No, v_First_Name, v_Last_Name, v_Hire_Date)
get_Employee_Info
DELIMITER $$
-- Thủ tục này lấy ra thông tin của nhân viên
-- Đầu vào: p_Emp_ID (Integer)
-- Có 4 tham số đầu ra v_Emp_No, v_First_Name, v_Last_Name, v_Hire_Date
CREATE PROCEDURE get_Employee_Info(p_Emp_ID Integer,
out v_Emp_No Varchar(50) ,
out v_First_Name Varchar(50) ,
Out v_Last_name Varchar(50) ,
Out v_Hire_date Date)
BEGIN
set v_Emp_No = concat( 'E' , Cast(p_Emp_Id as char(15)) );
--
set v_First_Name = 'Michael';
set v_Last_Name = 'Smith';
set v_Hire_date = curdate();
ENDThủ tục trên có 1 tham số đầu vào p_Emp_Id và 4 tham số đầu ra v_Emp_No, v_First_Name, v_Last_Name, v_Hire_Date, bạn gọi một thủ tục này từ Python truyền vào giá trị cho p_Emp_Id để lấy ra 4 giá trị đầu ra. Thật đáng tiếc giá trị nhận được không được đảm bảo đúng (Điều này được nói rõ trong đặc tả DB-API). Python chỉ có thể lấy ra các giá trị từ một mệnh đề SELECT.
Đặc tả DB-API:def callproc(self, procname, args=()): """Execute stored procedure procname with args procname -- string, name of procedure to execute on server args -- Sequence of parameters to use with procedure Returns the original args. Compatibility warning: PEP-249 specifies that any modified parameters must be returned. This is currently impossible as they are only available by storing them in a server variable and then retrieved by a query. Since stored procedures return zero or more result sets, there is no reliable way to get at OUT or INOUT parameters via callproc. The server variables are named @_procname_n, where procname is the parameter above and n is the position of the parameter (from zero). Once all result sets generated by the procedure have been fetched, you can issue a SELECT @_procname_0, ... query using .execute() to get any OUT or INOUT values. Compatibility warning: The act of calling a stored procedure itself creates an empty result set. This appears after any result sets generated by the procedure. This is non-standard behavior with respect to the DB-API. Be sure to use nextset() to advance through all result sets; otherwise you may get disconnected. """
Tuy vậy bạn vẫn có thể giải quyết được vấn đề ở trên, bạn cần phải bao bọc (wrap) thủ tục Get_Employee_Info ở trên bởi một thủ tục khác (Chẳng hạn Get_Employee_Info_Wrap), thủ tục này trả về các giá tri thông qua mệnh đề SELECT (Select clause).
get_Employee_Info_Wrap
DROP procedure IF EXISTS `get_Employee_Info_Wrap`;
DELIMITER $$
-- Thủ tục này bao bọc thủ tục Get_Employee_Info
CREATE PROCEDURE get_Employee_Info_Wrap(p_Emp_ID Integer,
out v_Emp_No Varchar(50) ,
out v_First_Name Varchar(50) ,
Out v_Last_name Varchar(50) ,
Out v_Hire_date Date)
BEGIN
Call get_Employee_Info( p_Emp_Id, v_Emp_No, v_First_Name, v_Last_Name, v_Hire_Date);
-- SELECT
Select v_Emp_No, v_First_Name, v_Last_Name, v_Hire_Date;
ENDThay vì gọi thủ tục Get_Employee_Info trong Python, hãy gọi thủ tục Get_Employee_Info_Wrap.
callProcedureExample.py
# Sử dụng module tiện ích của bạn.
import myconnutils
import datetime
connection = myconnutils.getConnection()
print ("Connect successful!")
try :
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Get_Employee_Info_Wrap
# @p_Emp_Id Integer ,
# @v_Emp_No Varchar(50) OUTPUT
# @v_First_Name Varchar(50) OUTPUT
# @v_Last_Name Varchar(50) OUTPUT
# @v_Hire_Date Date OUTPUT
v_Emp_No = ""
v_First_Name= ""
v_Last_Name= ""
v_Hire_Date = None
inOutParams = ( 100, v_Emp_No, v_First_Name , v_Last_Name, v_Hire_Date )
resultArgs = cursor.callproc("Get_Employee_Info_Wrap" , inOutParams )
print ('resultArgs:', resultArgs )
print ( 'inOutParams:', inOutParams )
print (' ----------------------------------- ')
for row in cursor:
print('Row: ', row )
print('Row[v_Emp_No]: ', row['v_Emp_No'] )
print('Row[v_First_Name]: ', row['v_First_Name'] )
print('Row[v_Last_Name]: ', row['v_Last_Name'] )
# datetime.date
v_Hire_Date = row['v_Hire_Date']
print('Row[v_Hire_Date]: ', v_Hire_Date )
finally:
# Đóng kết nối.
connection.close()Chạy ví dụ:
connect successful!
resultArgs: (100, '', '', '', None)
inOutParams: (100, '', '', '', None)
-----------------------------------
Row: {'v_Emp_No': 'E100', 'v_First_Name': 'Michael', 'v_Last_Name': 'Smith', 'v_Hire_Date': datetime.date(2017, 5, 17)}
Row[v_Emp_No]: E100
Row[v_First_Name]: Michael
Row[v_Last_Name]: Smith
Row[v_Hire_Date]: 2017-05-1710. Gọi Hàm
Để gọi hàm (function) trong Python, bạn nên tạo một câu truy vấn (query clause), và thực thi câu lệnh truy vấn này.
Dưới đây là hàm Get_Emp_No, tham số đầu vào là p_Emp_Id và trả về Emp_No (Mã nhân viên).
Get_Emp_No
DROP function if Exists `Get_Emp_No`;
DELIMITER $$
CREATE Function Get_Emp_No (p_Emp_Id Integer) Returns Varchar(50)
Begin
return concat('E', CAST(p_Emp_Id as char)) ;
END;callFunctionExample.py
# Sử dụng module tiện ích của bạn.
import myconnutils
import datetime
connection = myconnutils.getConnection()
print ("Connect successful!")
try :
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Get_Employee_Info_Wrap
# @p_Emp_Id Integer
v_Emp_No = ""
inOutParams = ( 100 )
sql = "Select Get_Emp_No(%s) as Emp_No "
cursor.execute(sql, ( 100 ) )
print (' ----------------------------------- ')
for row in cursor:
print('Row: ', row )
print('Row[Emp_No]: ', row['Emp_No'] )
finally:
# Đóng kết nối (Close connection).
connection.close()Chạy ví dụ:
connect successful!
-----------------------------------
Row: {'Emp_No': 'E100'}
Row[Emp_No]: E100Các hướng dẫn lập trình Python
- Tra cứu tài liệu Python
- Các lệnh rẽ nhánh trong Python
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Python Function
- Lớp và đối tượng trong Python
- Thừa kế và đa hình trong Python
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Python Dictionary
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Python Lists
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Python Tuples
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng Date Time trong Python
- Kết nối cơ sở dữ liệu MySQL trong Python sử dụng PyMySQL
- Hướng dẫn xử lý ngoại lệ trong Python
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ String trong Python
- Giới thiệu về Python
- Cài đặt Python trên Windows
- Cài đặt Python trên Ubuntu
- Cài đặt PyDev cho Eclipse
- Quy ước và các phiên bản ngữ pháp trong Python
- Hướng dẫn lập trình Python cho người mới bắt đầu
- Vòng lặp trong Python
Show More
