Mảng (Array) trong TypeScript
1. Mảng là gì?
Trong TypeScript mảng là một kiểu dữ liệu đặc biệt được sử dụng để lưu trữ nhiều giá trị của nhiều kiểu dữ liệu khác nhau. Khác với Java, mảng trong TypeScript có thể tự động mở rộng độ dài của nó nếu cần thiết.
Một mảng Type[] trong TypeScript có cách thức lưu trữ dữ liệu giống như Map<Integer,Type> trong Java. Chúng ta sẽ làm rõ điều này trong bài viết.
Giống với như JavaScript, TypeScript hỗ trợ 2 cú pháp để tạo một mảng:
Cú pháp Type[]
Cú pháp Type[] là cú pháp thông dụng để khai báo một mảng, nó được sử dụng trong nhiều ngôn ngữ khác nhau và tất nhiên bao gồm cả TypeScript:
Ví dụ: Khai báo một mảng chỉ để lưu trữ các phần tử kiểu string. Trình biên dịch của TypeScript sẽ thông báo lỗi nếu bạn vô tình thêm một phần tử kiểu khác vào mảng.
let fruits: string[];
fruits = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
// Or:
let fruits: string[] = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];Ví dụ: Khai báo một mảng với các phần tử có kiểu dữ liệu khác nhau:
let arr = [1, 3, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana', true, false];Ví dụ: Khai báo một mảng với kiểu dữ liệu liên hợp (union data type) - number và string:
let values: (string | number)[] = ['Apple', 'Orange', 1, 2, 'Banana', 3];Cú pháp Array<Type>
Khai báo một mảng dựa trên cú pháp Array<Type> cũng tương đương với cú pháp Type[], không có gì khác biệt.
let fruits: Array<string>;
fruits = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
// Or:
let fruits: Array<string> = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];Trong TypeScript, cú pháp Type[] chỉ là cách viết ngắn gọn của cú pháp Array<Type>. Các mảng trong TypeScript là các đối tượng của interface Array<T>, vì vậy chúng tuân thủ các tiểu chuẩn được định nghĩa trong interface này (Xem thêm tại phần dưới).
Ví dụ: Khai báo một mảng với kiểu dữ liệu liên hợp (union data type) - number và string:
let values: Array<string | number> = ['Apple', 'Orange', 1, 2, 'Banana', 3];2. Truy cập các phần tử của mảng
Các phần tử mảng có thể được truy cập bằng cách sử dụng chỉ số của một phần tử, ví dụ myArray[index]. Chỉ số mảng bắt đầu từ 0, vì vậy chỉ số của phần tử đầu tiên là 0, chỉ số của phần tử thứ hai là một, ...
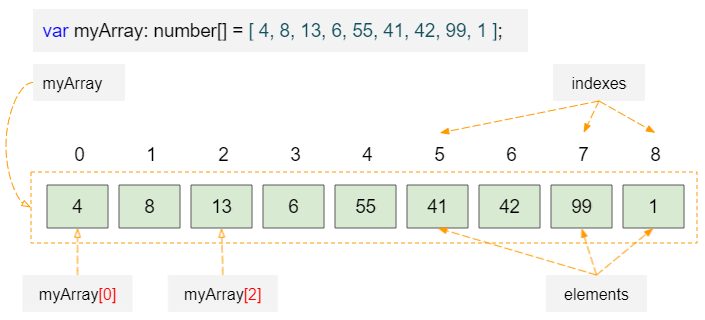
Ví dụ:
array_ex1.ts
function array_ex1_test() {
var myArray: number[] = [4, 8, 13, 6, 55, 41, 42, 99, 1];
console.log("Length of myArray: " + myArray.length); // 9 Elements
console.log("Element at index 0: " + myArray[0]); // 4
console.log("Element at index 1: " + myArray[1]); // 8
console.log("Element at index 4: " + myArray[4]); // 55
}
array_ex1_test(); // Call the functionOutput:
Length of myArray: 9
Element at index 0: 4
Element at index 1: 8
Element at index 4: 55Bạn cũng có thể gán giá trị mới cho các phần tử của mảng thông qua chỉ số của chúng:
array_ex2.ts
function array_ex2_test() {
var fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ];
console.log(`fruits[0] = ${fruits[0]}`);
console.log(`fruits[1] = ${fruits[1]}`);
console.log("--- Assign new values to elements ... --- ")
fruits[0] = "Breadfruit";
fruits[1] = "Carambola";
console.log(`fruits[0] = ${fruits[0]}`);
console.log(`fruits[1] = ${fruits[1]}`);
}
array_ex2_test(); // Call the function.Output:
fruits[0] = Acerola
fruits[1] = Apple
--- Assign new values to elements ... ---
fruits[0] = Breadfruit
fruits[1] = CarambolaKhác với Java, mảng trong TypeScript có thể tự động tăng độ dài nếu cần thiết. Trong ví dụ dưới đây chúng ta có một mảng với độ dài ban đầu là 3. Chúng ta gán giá trị cho các phần tử tại chỉ số 6 và 7. Lúc này, độ dài của mảng sẽ là 8.
array_ex3.ts
function array_ex3_test() {
var fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ];
console.log(`Array length is ${fruits.length}`); // 3
console.log(" --- Set the value for the elements at index 6 and 7. ---");
// Add more elements to the array.
fruits[6] = "Breadfruit";
fruits[7] = "Carambola";
console.log(`Now Array length is ${fruits.length}`); // 8 indexes: [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
console.log(`Element at index 4: ${fruits[4]}`); // undefined
console.log(`Element at index 5: ${fruits[5]}`); // undefined
}
array_ex3_test(); // Call the function.Output:
Array length is 3
--- Set the value for the elements at index 6 and 7. ---
Now Array length is 8
Element at index 4: undefined
Element at index 5: undefined3. Chỉ số không nguyên
Khác với Java và C#. Mảng trong TypeScript chấp nhận các chỉ số không phải là số nguyên, nó cũng chấp nhận các chỉ số là số âm. Tuy nhiên các phần tử như vậy không được tính vào độ dài của mảng.
array_idx_ex1.ts
function array_idx_ex1_test() {
var fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ];
console.log(`Array length is ${fruits.length}`); // 3
console.log(" --- Set the value for the elements at indexes 6, 10.5 and -100 ---");
// Add more elements to the array.
fruits[6] = "Breadfruit";
fruits[10.5] = "Carambola"; // !!!!!!!!!!
fruits[-100] = "Grapefruit"; // !!!!!!!!!!
console.log(`Now Array length is ${fruits.length}`); // 7 indexes: [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
console.log(`Element at index 4: ${fruits[4]}`); // undefined
console.log(`Element at index 5: ${fruits[5]}`); // undefined
console.log(`Element at index 10.5: ${fruits[10.5]}`); // Carambola
console.log(`Element at index -100: ${fruits[-100]}`); // Grapefruit
}
array_idx_ex1_test(); // Call the function.Output:
Array length is 3
--- Set the value for the elements at indexes 6, 10.5 and -100 ---
Now Array length is 7
Element at index 4: undefined
Element at index 5: undefined
Element at index 10.5: Carambola
Element at index -100: Grapefruit4. Vòng lặp trên mảng
Về cơ bản có hai cú pháp vòng lặp for để truy cập vào các phần tử của mảng.
Syntax 1:
Cú pháp này chỉ cho phép truy cập vào các phần tử với chỉ số là số nguyên không âm.
for(let idx =0; idx < fruits.length; idx++) {
console.log(`Element at index ${idx} is ${fruits[idx]}`);
}Ví dụ:
array_for_loop_ex1.ts
function array_for_loop_ex1_test() {
var fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ];
console.log(`Array length is ${fruits.length}`); // 3 indexes [0,1,2]
console.log(" --- Set the value for the elements at indexes 6 and 10.5 ---");
// Add more elements to the array.
fruits[6] = "Breadfruit";
fruits[10.5] = "Carambola"; // !!!!!!!!!!
for(let idx =0; idx < fruits.length; idx++) {
console.log(`Element at index ${idx} is ${fruits[idx]}`);
}
}
array_for_loop_ex1_test(); // Call the function.Output:
Element at index 0 is Acerola
Element at index 1 is Apple
Element at index 2 is Banana
Element at index 3 is undefined
Element at index 4 is undefined
Element at index 5 is undefined
Element at index 6 is BreadfruitSyntax 2:
Cú pháp vòng lặp for dưới đây chỉ truy cập vào các chỉ số thực sự tồn tại trong mảng, kể cả các chỉ số không phải là số nguyên hoặc số âm.
for(let idx in fruits) {
console.log(`Element at index ${idx} is ${fruits[idx]}`);
}Ví dụ:
array_for_loop_ex2.ts
function array_for_loop_ex2_test() {
var fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ];
console.log(`Array length is ${fruits.length}`); // 3 indexes [0,1,2]
console.log(" --- Set the value for the elements at indexes 6 and 10.5 ---");
// Add more elements to the array.
fruits[6] = "Breadfruit";
fruits[10.5] = "Carambola"; // !!!!!!!!!!
for(let idx in fruits) {
console.log(`Element at index ${idx} is ${fruits[idx]}`);
}
}
array_for_loop_ex2_test(); // Call the function.Output:
Element at index 0 is Acerola
Element at index 1 is Apple
Element at index 2 is Banana
Element at index 6 is Breadfruit
Element at index 10.5 is CarambolaOther Examples:
Ví dụ: Một mảng chứa các phần tử kiểu string, chuyển đổi tất cả các phần tử của nó thành chữ hoa (uppercase).
array_for_loop_ex3.ts
function array_for_loop_ex3_test() {
var fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ];
for(let idx in fruits) {
let v = fruits[idx];
if(v) {
fruits[idx] = v.toUpperCase();
}
}
// Print elements:
for(let idx in fruits) {
console.log(`Element at index ${idx} is ${fruits[idx]}`);
}
}
array_for_loop_ex3_test(); // Call the function.Output:
Element at index 0 is ACEROLA
Element at index 1 is APPLE
Element at index 2 is BANANA5. Mảng chỉ đọc
Sử dụng từ khoá readonly trong khai báo một mảng để tạo một mảng chỉ đọc (read only). Điều này có nghĩa là bạn không thể thêm, xoá, hoặc cập nhập các phần tử của mảng.
- Chú ý: Từ khoá readonly chỉ được phép xuất hiện trong cú pháp Type[], không áp dụng với cú pháp Array<Type>.
let okArray1 : readonly string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ]; // OK
let okArray2 : readonly string[];
okArray2 = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ]; // OK
let errorArray1 : readonly Array<String>; // Compile Error!!!Không cần sử dụng từ khoá readonly, bạn cũng có thể khai báo một mảng chỉ đọc (read only) với interface ReadonlyArray<T>:
let okArray3 : ReadonlyArray<String>; // OKVí dụ:
let fruits: readonly string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ]; // OK
fruits[1] = "Breadfruit"; // Compile Error!!!!!!
let years: ReadonlyArray<number> = [2001, 2010, 2020 ]; // OK
years[1] = 2021; // Compile Error!!!!!!6. Các phương thức của mảng
Trong TypeScript, mảng là đối tượng của interface Array<T>, vì vậy nó có các phương thức được định nghĩa trong interface này.
interface Array<T> {
length: number;
toString(): string;
toLocaleString(): string;
pop(): T | undefined;
push(...items: T[]): number;
concat(...items: ConcatArray<T>[]): T[];
concat(...items: (T | ConcatArray<T>)[]): T[];
join(separator?: string): string;
reverse(): T[];
shift(): T | undefined;
slice(start?: number, end?: number): T[];
sort(compareFn?: (a: T, b: T) => number): this;
splice(start: number, deleteCount?: number): T[];
splice(start: number, deleteCount: number, ...items: T[]): T[];
unshift(...items: T[]): number;
indexOf(searchElement: T, fromIndex?: number): number;
lastIndexOf(searchElement: T, fromIndex?: number): number;
every<S extends T>(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => value is S, thisArg?: any): this is S[];
every(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): boolean;
some(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): boolean;
forEach(callbackfn: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => void, thisArg?: any): void;
map<U>(callbackfn: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => U, thisArg?: any): U[];
filter<S extends T>(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => value is S, thisArg?: any): S[];
filter(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): T[];
reduce(callbackfn: (previousValue: T, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => T): T;
reduce(callbackfn: (previousValue: T, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => T, initialValue: T): T;
reduce<U>(callbackfn: (previousValue: U, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => U, initialValue: U): U;
reduceRight(callbackfn: (previousValue: T, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => T): T;
reduceRight(callbackfn: (previousValue: T, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => T, initialValue: T): T;
reduceRight<U>(callbackfn: (previousValue: U, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => U, initialValue: U): U;
[n: number]: T;
}7. forEach(..)
forEach(callbackfn: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => void, thisArg?: any): void;Thực hiện hành động được chỉ định cho mỗi phần tử trong một mảng.
Ví dụ:
array_forEach_ex1.ts
function array_forEach_ex1_test() {
let fruits: string[] = ["Acerola", "Apple", "Banana" ]; // OK
// A callback function.
var callback = function(value:string, index:number, thisArray:string[]) {
if(index % 2 == 0) {
console.log(value);
} else {
console.log(value.toUpperCase());
}
}
fruits.forEach(callback);
}
array_forEach_ex1_test(); // Call the function.Output:
Acerola
APPLE
Banana8. every(..)
every(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): boolean;Kiểm tra xem tất cả các phần tử của mảng có vượt qua kiểm tra của một hàm được chỉ định hay không.
predicate: Là hàm để kiểm tra từng phần tử của mảng.
Ví dụ: Một mảng bao gồm các năm. Kiểm tra xem tất cả các năm lớn hơn 1990 hay không.
array_every_ex1.ts
function array_every_ex1_test() {
let years: number[] = [2001, 1995, 2007, 2010, 2020];
// Arrow function.
var predicate = (value: number, index: number, thisArray: number[]) => {
return value > 1990;
}
var ok: boolean = years.every(predicate);
console.log(`All years > 1990? ${ok}`); // true
}
array_every_ex1_test(); // Call the function.9. sort(..)
sort(compareFn?: (a: T, b: T) => number): this;Sắp xếp mảng này dựa trên hàm được chỉ định và trả về mảng này. Nếu hàm không được cung cấp, các phần tử của mảng sẽ được sắp xếp theo quy tắc tự tự nhiên.
Ví dụ: Sắp xếp một mảng string:
array_sort_ex1.ts
function array_sort_ex1_test() {
let fruits: string[] = ["Banana", "Acerola", "Apple", "Carambola", "Breadfruit"];
// Compare Function:
var compareFn = (a: string, b: string) => {
// v > 0 --> a > b
// v = 0 --> a == b
// v < 0 --> a < b
let v: number = a.localeCompare(b);
return v;
}
fruits.sort(compareFn);
console.log("--- after sorting --- ");
console.log(fruits);
}
array_sort_ex1_test(); // Call the function.Output:
--- after sorting ---
[ 'Acerola', 'Apple', 'Banana', 'Breadfruit', 'Carambola' ]10. filter(..)
filter(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): T[];
filter<S extends T>(predicate: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => value is S, thisArg?: any): S[];Trả về một mảng mới bao gồm các phần tử vượt qua kiểm tra của một hàm được chỉ định.
Ví dụ: Một mảng bao gồm các năm, lọc ra một mảng mới chỉ bao gồm các năm chẵn.
array_filter_ex1.ts
function array_filter_ex1_test() {
let years: number[] = [2001, 1995, 2007, 2010, 2020];
// Filter even value.
var predicate = (value: number, index: number, thisArray: number[]) => {
return value % 2 == 0;
}
var evenYears: number[] = years.filter(predicate);
console.log(" --- Even Years: --- ");
console.log(evenYears);
}
array_filter_ex1_test(); // Call the function.Output:
--- Even Years: ---
[ 2010, 2020 ]Các hướng dẫn TypeScript
- Chạy ví dụ TypeScript đầu tiên của bạn trong Visual Studio Code
- Không gian tên (Namespace) trong TypeScript
- Module trong TypeScript
- Toán tử typeof trong TypeScript
- Biến (Variable) trong TypeScript
- Vòng lặp trong TypeScript
- Cài đặt TypeScript trên Windows
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ hàm trong TypeScript
- Tuples trong TypeScript
- Interface trong TypeScript
- Mảng (Array) trong TypeScript
- Toán tử instanceof trong TypeScript
- Phương thức trong TypeScript
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ TypeScript Closures
- Constructor trong TypeScript
- Property trong TypeScript
- Phân tích JSON trong TypeScript
- Phân tích JSON trong TypeScript với thư viện json2typescript
- Trình chuyển đổi mã nguồn (Transpiler) là gì?
Show More
