Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectOutputStream
1. ObjectOutputStream
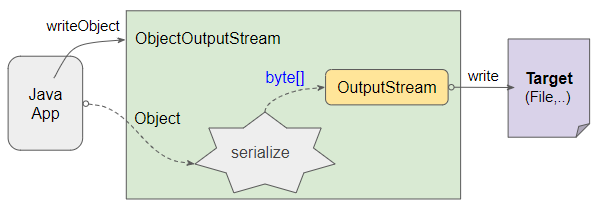
ObjectOutputStream là một lớp con của lớp OutputStream. Nó quản lý một đối tượng OutputStream và cung cấp các phương thức để ghi dữ liệu nguyên thuỷ (primitive data) hoặc đối tượng vào OutputStream mà nó quản lý.
public class ObjectOutputStream
extends OutputStream implements ObjectOutput, ObjectStreamConstantsObjectInputStream được sử dụng để đọc các nguồn dữ liệu được tạo ra bởi ObjectOutputStream:
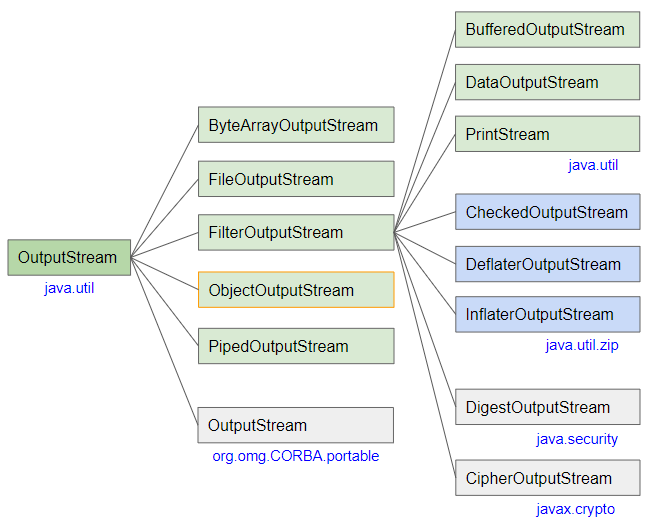
- OutputStream
- FilterOutputStream
- ByteArrayOutputStream
- PrintStream
- PipedOutputStream
- BufferedOutputStream
- DataOutputStream
- FileInputStream
- CheckedOutputStream
- CheckedOutputStream
- CipherOutputStream
- DeflaterOutputStream
- DigestOutputStream
- InflaterOutputStream
ObjectOutputStream Methods
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException
public void writeBoolean(boolean val) throws IOException
public void writeByte(int val) throws IOException
public void writeShort(int val) throws IOException
public void writeChar(int val) throws IOException
public void writeInt(int val) throws IOException
public void writeLong(long val) throws IOException
public void writeFloat(float val) throws IOException
public void writeDouble(double val) throws IOException
public void writeBytes(String str) throws IOException
public void writeChars(String str) throws IOException
public void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException
public void writeUnshared(Object obj) throws IOException
public void writeFields() throws IOException
public void defaultWriteObject() throws IOException
public void useProtocolVersion(int version) throws IOException
public ObjectOutputStream.PutField putFields() throws IOException
public void reset() throws IOException
protected void writeObjectOverride(Object obj) throws IOException
protected void annotateClass(Class<?> cl) throws IOException
protected void annotateProxyClass(Class<?> cl) throws IOException
protected Object replaceObject(Object obj) throws IOException
protected boolean enableReplaceObject(boolean enable) throws SecurityException
protected void writeStreamHeader() throws IOException
protected void writeClassDescriptor(ObjectStreamClass desc) throws IOException
protected void drain() throws IOException
int getProtocolVersion()
void writeTypeString(String str) throws IOException
// Methods Inherited from OutputStream
public void write(int val) throws IOException
public void write(byte[] buf) throws IOException
public void write(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException
public void flush() throws IOException
public void close() throws IOExceptionObjectOutputStream Constructors
ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)Các đối tượng cần được tuần tự hoá (serialized) trước khi được ghi vào ObjectOutputStream, các đối tượng này phải thực thi (implement) giao diện Serializable.
2. Example 1
Lớp Employee thi hành (implement) interface Serializable, điều này là cần thiết để nó có thể được ghi vào ObjectOutputStream.
Employee.java
package org.o7planning.beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String fullName;
private float salary;
public Employee(String fullName, float salary) {
this.fullName = fullName;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public void setFullName(String firstName) {
this.fullName = firstName;
}
public float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(float lastName) {
this.salary = lastName;
}
}Ví dụ, Sử dụng ObjectOutputStream để ghi các đối tượng Employee vào một file.
WriteEmployeeDataEx.java
package org.o7planning.objectoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.beans.Employee;
public class WriteEmployeeDataEx {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/employees.data
private static String file_path = "/Volumes/Data/test/employees.data";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File outFile = new File(file_path);
outFile.getParentFile().mkdirs();
Employee e1 = new Employee("Tom", 1000f);
Employee e2 = new Employee("Jerry", 2000f);
Employee e3 = new Employee("Donald", 1200f);
Employee[] employees = new Employee[] { e1, e2, e3 };
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
System.out.println("Writing file: " + outFile.getAbsolutePath());
oos.writeObject(new Date());
oos.writeUTF("Employee data"); // Some informations.
oos.writeInt(employees.length); // Number of Employees
for (Employee e : employees) {
oos.writeObject(e);
}
oos.close();
System.out.println("Finished!");
}
}Sau khi chạy lớp WriteEmployeeDataEx chúng ta nhận được một file với nội dung khá khó hiểu, để đọc nội dung của nó bạn phải sử dụng lớp ObjectInputStream.
OK, Đọc file vừa được ghi ra ở bước trước với ObjectInputStream.
ReadEmployeeDataEx.java
package org.o7planning.objectoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.beans.Employee;
public class ReadEmployeeDataEx {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/employees.data
private static String file_path = "/Volumes/Data/test/employees.data";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File inFile = new File(file_path);
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(inFile);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
System.out.println("Reading file: " + inFile.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println();
Date date = (Date) ois.readObject();
String info = ois.readUTF();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(info);
System.out.println();
int employeeCount = ois.readInt();
for(int i=0; i< employeeCount; i++) {
Employee e = (Employee) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("Employee Name: " + e.getFullName() +" / Salary: " + e.getSalary());
}
ois.close();
}
}Output:
Reading file: /Volumes/Data/test/employees.data
Sat Mar 20 18:54:24 KGT 2021
Employee data
Employee Name: Tom / Salary: 1000.0
Employee Name: Jerry / Salary: 2000.0
Employee Name: Donald / Salary: 1200.03. Example 2
Hầu hết các lớp trong Java Collection Framework đều thi hành giao diện Serializable, chẳng hạn ArrayList, LinkedList, HashMap, LinkedHashMap, TreeMap,... vì vậy đối tượng của chúng có thể ghi được vào ObjectOutputStream.
Ví dụ, ghi một đối tượng ArrayList vào file.
Chú ý: Tất cả các phần tử của ArrayList phải là kiểu Serializable.
WriteListEx1.java
package org.o7planning.objectoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WriteListEx1 {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/flowers.data
private static String file_path = "/Volumes/Data/test/flowers.data";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
writeFile();
readFile();
}
private static void writeFile() throws IOException {
ArrayList<String> flowers = new ArrayList<String>();
flowers.add("Tulip");
flowers.add("Daffodil");
flowers.add("Poppy");
flowers.add("Sunflower");
flowers.add("Bluebell");
File file = new File(file_path);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
// Write a String
oos.writeUTF("A list of flowers");
// Write an Object
oos.writeObject(flowers);
oos.close();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static void readFile() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file = new File(file_path);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
// Read a String
String info = ois.readUTF();
// Read an Object
List<String> flowers = (List<String>) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(info);
System.out.println();
for (String s : flowers) {
System.out.println(s);
}
ois.close();
}
}Output:
A list of flowers
Tulip
Daffodil
Poppy
Sunflower
Bluebell4. writeFields()
Giả sử bạn có một đối tượng GameSetting và bạn muốn ghi đối tượng này vào ObjectOutputStream, nhưng không phải tất cả các trường (field) của nó.
GameSetting.java
package org.o7planning.beans;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class GameSetting implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int sound;
private int bightness;
private String difficultyLevel;
private String userNote;
public GameSetting(int sound, int bightness, String difficultyLevel, String userNote) {
this.sound = sound;
this.bightness = bightness;
this.difficultyLevel = difficultyLevel;
this.userNote = userNote;
}
public int getSound() {
return sound;
}
public int getBightness() {
return bightness;
}
public String getDifficultyLevel() {
return difficultyLevel;
}
public String getUserNote() {
return userNote;
}
// Do not change name and parameter of this method.
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream.PutField fields = out.putFields();
// Write this object with custom fields
fields.put("sound", this.sound < 20 ? 20 : this.sound);
fields.put("bightness", this.bightness < 30 ? 30 : this.bightness);
fields.put("difficultyLevel", this.difficultyLevel);
// Do not write "userNote".
// fields.put("userNote", this.userNote);
out.writeFields();
}
}ObjectOutputStream_writeFields.java
package org.o7planning.objectoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.beans.GameSetting;
public class ObjectOutputStream_writeFields {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/game_setting.data
private static String file_path = "/Volumes/Data/test/game_setting.data";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
GameSetting setting = new GameSetting(10, 80, "Hard", "Try game again!");
writeGameSetting(setting);
readGameSetting();
}
private static void writeGameSetting(GameSetting setting) throws IOException {
File file = new File(file_path);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
// Write a String
oos.writeUTF("Game Settings, Save at " + new Date());
// Write Object
oos.writeObject(setting);
oos.close();
}
private static void readGameSetting() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file = new File(file_path);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
// Read a String
String info = ois.readUTF();
// Read fields
GameSetting setting = (GameSetting) ois.readObject();
System.out.println("sound: " + setting.getSound());
System.out.println("bightness: " + setting.getBightness());
System.out.println("difficultyLevel: " + setting.getDifficultyLevel());
System.out.println("userNote: " + setting.getUserNote()); // null.
ois.close();
}
}Output:
sound: 20
bightness: 80
difficultyLevel: Hard
userNote: nullXem thêm về phương thức ObjectInputStream.readFields():
5. writeUnshared(Object)
Phương thức writeUnshared(Object) làm việc giống như phương thức writeObject(Object) nhưng khác biệt trong tình huống sau đây:
Giả sử bạn muốn ghi đối tượng "X" hai lần vào một ObjectOutputStream điều gì sẽ xẩy ra?
|
|
|
|
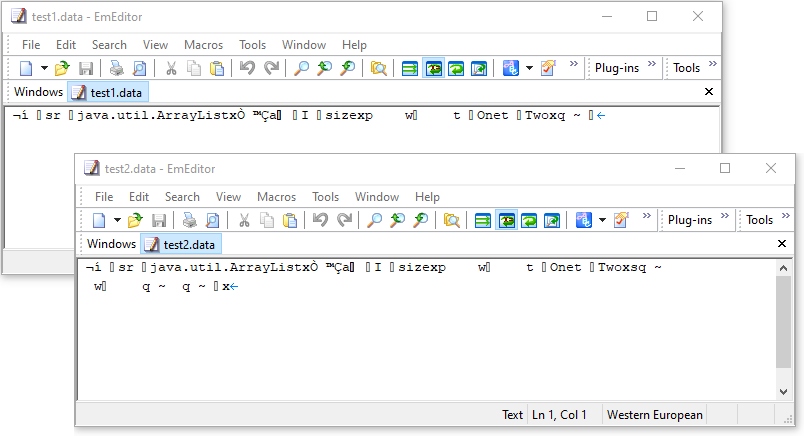
Ví dụ, sử dụng phương thức writeObject để ghi hai lần một đối tượng ArrayList vào một file. Và sử dụng phương thức writeUnshared để ghi hai lần một đối tượng ArrayList vào một file khác. File thứ hai sẽ có kích thước lớn hơn.
ObjectOutputStream_writeUnshared.java
package org.o7planning.objectoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ObjectOutputStream_writeUnshared {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/test1.data
private static String file_path1 = "/Volumes/Data/test/test1.data";
private static String file_path2 = "/Volumes/Data/test/test2.data";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
writeObjectTest();
writeUnsharedTest();
}
private static void writeObjectTest() throws IOException {
File file = new File(file_path1);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("One");
list.add("Two");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(list); // Write the first time
oos.writeObject(list); // Write the second time
oos.close();
}
private static void writeUnsharedTest() throws IOException {
File file = new File(file_path2);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("One");
list.add("Two");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeUnshared(list); // Write the first time
oos.writeUnshared(list); // Write the second time
oos.close();
}
}Output:
Các hướng dẫn Java IO
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java CharArrayWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FilterReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FilterWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PrintStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java StringReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java StringWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java LineNumberReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PushbackReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PrintWriter
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng luồng vào ra nhị phân trong Java
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng luồng vào ra ký tự trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ByteArrayOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java OutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PushbackInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java SequenceInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Reader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Writer
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java CharArrayReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ByteArrayInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java InputStreamReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java OutputStreamWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java InputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileInputStream
Show More
- Hướng dẫn lập trình Java Servlet/JSP
- Các hướng dẫn Java New IO
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Cloud
- Các hướng dẫn Java Oracle ADF
- Các hướng dẫn Java Collections Framework
- Java cơ bản
- Các hướng dẫn Java Date Time
- Các thư viện mã nguồn mở Java
- Các hướng dẫn Java Web Services
- Các hướng dẫn Struts2 Framework
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Boot
