Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataOutputStream
1. DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream thường được sử dụng để ghi các dữ liệu nguyên thuỷ (primitive data) vào một OutputStream khác. Sau đó, một ứng dụng có thể sử dụng DataInputStream để đọc dữ liệu trở lại.
public class DataOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream implements DataOutputDataOutputStream được khuyến khích sử dụng để ghi các dữ liệu dạng bảng, giống như Excel. (Xem ví dụ ở giữa bài viết này).
OrderDate | Finished | Item | Units | UnitCost | Total |
2020-01-06 | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | |
2020-01-23 | Binder | 50 | 19.99 | 999.50 | |
2020-02-09 | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | |
2020-02-26 | Pen | 27 | 19.99 | 539.73 | |
2020-03-15 | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 |
- ByteArrayOutputStream
- FileOutputStream
- FilterOutputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
- PipedOutputStream
- BufferedOutputStream
- OutputStream
- PrintStream
- CheckedOutputStream
- CipherOutputStream
- DeflaterOutputStream
- DigestOutputStream
- InflaterOutputStream
3. Methods
public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException
public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException
public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOException
public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOException
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException
public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOException
public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException
public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException
public final void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException
public final void writeChars(String s) throws IOException
public final void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException
public final int size()Các phương thức khác thừa kế từ các lớp cha:
public static OutputStream nullOutputStream()
public void write(int b) throws IOException
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException
public void flush() throws IOException
public void close() throws IOException4. Examples
DataOutputStream thường được sử dụng để ghi các dữ liệu có cấu trúc kiểu như Excel. Bây giờ, chúng ta sẽ ghi bảng dữ liệu dưới đây vào 1 file:
OrderDate | Finished | Item | Units | UnitCost | Total |
2020-01-06 | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | |
2020-01-23 | Binder | 50 | 19.99 | 999.50 | |
2020-02-09 | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | |
2020-02-26 | Pen | 27 | 19.99 | 539.73 | |
2020-03-15 | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 |
Đầu tiên, viết lớp Order mô phỏng dữ liệu của một dòng của bảng:
Order.java
package org.o7planning.dataoutputstream.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class Order {
private LocalDate orderDate;
private boolean finished;
private String item;
private int units;
private float unitCost;
private float total;
public Order(LocalDate orderDate, boolean finished, //
String item, int units, float unitCost, float total) {
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.finished = finished;
this.item = item;
this.units = units;
this.unitCost = unitCost;
this.total = total;
}
public LocalDate getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public boolean isFinished() {
return finished;
}
public String getItem() {
return item;
}
public int getUnits() {
return units;
}
public float getUnitCost() {
return unitCost;
}
public float getTotal() {
return total;
}
}Tiếp theo, sử dụng DataOutputStream để ghi bảng dữ liệu trên vào một file:
WriteDataFile_example1.java
package org.o7planning.dataoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class WriteDataFile_example1 {
// Windows: C:/somepath/data-file.txt
private static final String filePath = "/Volumes/Data/test/data-file.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Order[] orders = new Order[] { //
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 6), true, "Pencil", 95, 1.99f, 189.05f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 23), false, "Binder", 50, 19.99f, 999.50f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 2, 9), true, "Pencil", 36, 4.99f, 179.64f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 2, 26), false, "Pen", 27, 19.99f, 539.73f),
new Order(LocalDate.of(2020, 3, 15), true, "Pencil", 56, 2.99f, 167.44f) //
};
File outFile = new File(filePath);
outFile.getParentFile().mkdirs();
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
for (Order order : orders) {
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(order.getOrderDate().toString());
dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(order.isFinished());
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(order.getItem());
dataOutputStream.writeInt(order.getUnits());
dataOutputStream.writeFloat(order.getUnitCost());
dataOutputStream.writeFloat(order.getTotal());
}
dataOutputStream.close();
}
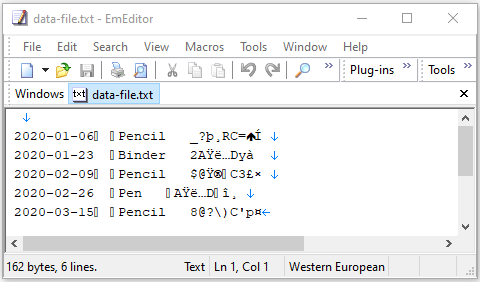
}Sau khi chạy ví dụ trên chúng ta có một file dữ liệu, nội dung của nó khá khó hiểu:
Cuối cùng, chúng ta sử dụng DataInputStream để đọc file nói trên.
ReadDataFile_example1.java
package org.o7planning.dataoutputstream.ex;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ReadDataFile_example1 {
// Windows: C:/somepath/data-file.txt
private static final String filePath = "/Volumes/Data/test/data-file.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);
int row = 0;
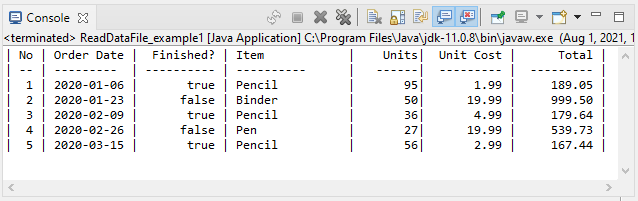
System.out.printf("|%3s | %-10s | %10s | %-15s | %8s| %10s | %10s |%n", //
"No", "Order Date", "Finished?", "Item", "Units", "Unit Cost", "Total");
System.out.printf("|%3s | %-10s | %10s | %-15s | %8s| %10s | %10s |%n", //
"--", "---------", "----------", "----------", "------", "---------", "---------");
while (dataInputStream.available() > 0) {
row++;
String orderDate = dataInputStream.readUTF();
boolean finished = dataInputStream.readBoolean();
String item = dataInputStream.readUTF();
int units = dataInputStream.readInt();
float unitCost = dataInputStream.readFloat();
float total = dataInputStream.readFloat();
System.out.printf("|%3d | %-10s | %10b | %-15s | %8d| %,10.2f | %,10.2f |%n", //
row, orderDate, finished, item, units, unitCost, total);
}
dataInputStream.close();
}
}Output:
5. writeBytes(String s)
Chuyển đổi String đã cho thành dẫy các ký tự, sau đó ép kiểu (cast) từng ký tự thành byte và ghi vào DataOutputStream này bằng phương thức writeByte(byte).
public final void writeBytes(String s) throws IOExceptionViệc gọi phương thức writeBytes(String) tương đương với:
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
out.write((byte)s.charAt(i));
}
incCount(len);6. writeChars(String s)
Chuyển đổi String đã cho thành dẫy các ký tự, sau đó ghi lần lượt từng ký tự vào DataOutputStream này bằng phương thức writeChar(char).
public final void writeChars(String s) throws IOExceptionViệc gọi phương thức writeChars(String) tương đương với:
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
int v = s.charAt(i);
writeChar(v);
}7. writeUTF(String str)
Ghi một String vào DataOutputStream này với mã hoá "Modified UTF-8" (UTF-8 đã được sửa đổi).
public final void writeUTF(String str) throws IOExceptionĐầu tiên, hai bytes được ghi vào luồng đầu ra như thể bằng phương thức writeShort cho biết số bytes theo sau. Giá trị này là số bytes thực sự được viết ra, không phải là độ dài của chuỗi.
Chẳng hạn, gọi phương thức writeUTF("ÂBC") để ghi chuỗi "ÂBC". Như đã biết, UTF-8 sử dụng 1, 2, 3 hoặc 4 bytes để lưu trữ một ký tự.
- 'Â' --> 2 bytes
- 'B' --> 1 byte
- 'C' --> 1 byte
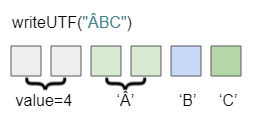
Đầu tiên, 2 bytes được sử dụng để lưu thông tin số bytes cần thiết để lưu trữ chuỗi này. 4 bytes tiếp theo được sử dụng để ghi chuỗi "ÂBC" theo mã hoá "Modified UTF-8".
- UTF-8
- DataInputStream
8. writeBoolean(boolean v)
public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeBoolean(boolean) ghi một giá trị boolean vào DataOutputStream này. Nếu giá trị này là true thì (byte)1 sẽ được ghi vào, ngược lại (byte)0 sẽ được ghi vào.
9. writeByte(int v)
public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOExceptionGhi một byte vào DataOutputStream này.
10. writeShort(int v)
public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeShort(int) ghi 2 bytes vào DataOutputStream này.
Hai bytes được ghi vào là:
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 8))
(byte)(0xff & v)11. writeChar(int v)
public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeChar(int) ghi 2 bytes vào DataOutputStream này.
Hai bytes được ghi vào là:
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 8))
(byte)(0xff & v)12. writeInt(int v)
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeInt(int) ghi 4 bytes vào DataOutputStream này.
Bốn bytes được ghi vào là:
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 24))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 16))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 8))
(byte)(0xff & v)13. writeLong(long v)
public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeLong(long) ghi 8 bytes vào DataOutputStream này.
Tám bytes được ghi vào là:
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 56))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 48))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 40))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 32))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 24))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 16))
(byte)(0xff & (v >> 8))
(byte)(0xff & v)14. writeFloat(float v)
public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeFloat(float) ghi 4 bytes vào DataOutputStream này.
15. writeDouble(double v)
public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOExceptionPhương thức writeDouble(double) ghi 8 bytes vào DataOutputStream này.
16. size()
Trả về số bytes đã được ghi vào DataOutputStream này, hoặc trả về Integer.MAX_VALUE nếu giá trị thực sự lớn hơn.
public final int size()Ví dụ:
DataOutputStream_size_ex1.java
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);
dos.writeByte(111);
System.out.println("Number of bytes: " + dos.size()); // 1
// 1 char = 2 bytes.
dos.writeChars("ÂBC");
System.out.println("Number of bytes: " + dos.size()); // 1 + 2*3 = 7
// 1 char = 2 bytes.
dos.writeChar('A');
System.out.println("Number of bytes: " + dos.size()); // 7 + 2 = 9
// In UTF-8:
// Two bytes of length information is added before the UTF-8 String (See writeUTF methods).
// UTF-8 String: "ÂBC" =4 bytes; 'Â' = 2 bytes, 'B' = 1 byte, 'C' = 1 byte.
dos.writeUTF("ÂBC");
System.out.println("Number of bytes: " + dos.size()); // 9 + 2 + 4 = 15Các hướng dẫn Java IO
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java CharArrayWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FilterReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FilterWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PrintStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java StringReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java StringWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java LineNumberReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PushbackReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PrintWriter
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng luồng vào ra nhị phân trong Java
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng luồng vào ra ký tự trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ByteArrayOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java OutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PushbackInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java SequenceInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Reader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Writer
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java CharArrayReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ByteArrayInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java InputStreamReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java OutputStreamWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java InputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileInputStream
Show More
- Hướng dẫn lập trình Java Servlet/JSP
- Các hướng dẫn Java New IO
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Cloud
- Các hướng dẫn Java Oracle ADF
- Các hướng dẫn Java Collections Framework
- Java cơ bản
- Các hướng dẫn Java Date Time
- Các thư viện mã nguồn mở Java
- Các hướng dẫn Java Web Services
- Các hướng dẫn Struts2 Framework
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Boot
