Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedInputStream
1. PipedInputStream
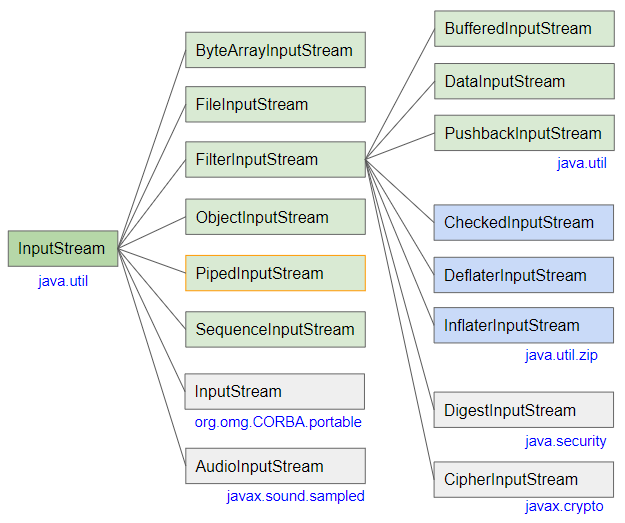
- InputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- SequenceInputStream
- FileInputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream
- ObjectInputStream
- PushbackInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- AudioInputStream
- DataInputStream
- InflaterInputStream
- DigestInputStream
- DeflaterInputStream
- CipherInputStream
- CheckedInputStream
Để dễ dàng hiểu về PipedInputStream tôi đưa ra một tình huống như hình minh hoạ dưới đây:
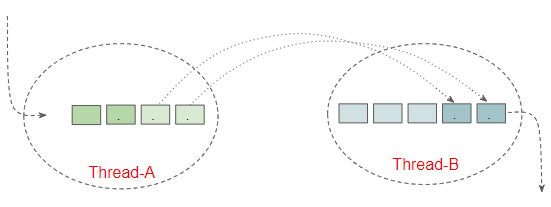
Giả sử bạn đang phát triển một ứng dụng Multithreading (Đa luồng), và bạn có 2 Thread độc lập là Thread-A và Thread-B. Câu hỏi đặt ra là:
- Cần làm gì để mỗi khi các bytes xuất hiện trên Thread-A chúng sẽ được chuyển sang Thread-B một cách tự động?
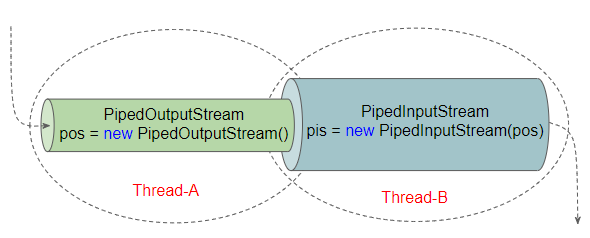
PipedOutputStream và PipedInputStream được tạo ra giúp bạn xử lý tình huống đề cập ở trên. Mỗi khi dữ liệu được ghi vào PipedOutputStream chúng sẽ xuất hiện một cách tự động trên PipedInputStream.
PipedInputStream constructors
PipedInputStream()
PipedInputStream(int pipeSize)
PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src)
PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src, int pipeSize)Để dữ liệu ghi vào PipedOutputStream xuất hiện trên PipedInputStream bạn phải kết nối (connect) hai đối tượng này với nhau.
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
pipedOS.connect(pipedIS);Code trên cũng tương đương với các cách dưới đây:
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
pipedIS.connect(pipedOS);PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream(pipedOS);PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream(pipedIS);- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedWriter
2. Example 1
PipedInputStreamEx1.java
package org.o7planning.pipedinputstream.ex;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class PipedInputStreamEx1 {
private PipedInputStream pipedIS;
private PipedOutputStream pipedOS;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
new PipedInputStreamEx1().test();
}
private void test() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// Create a PipedInputStream
pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
// Data written to 'pipedOS'
// will appear automatically at 'pipedIS'.
pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream(pipedIS);
new ThreadB().start();
new ThreadA().start();
}
//
class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 'a', 97, 'b', 'c', 101 };
for (byte b : bytes) {
pipedOS.write(b);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(pipedOS);
}
}
}
//
class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int b = 0;
while ((b = pipedIS.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(b + " " + (char) b);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(pipedIS);
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(InputStream in) {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(OutputStream out) {
if (out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}Output:
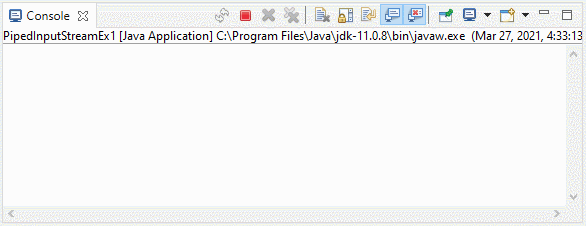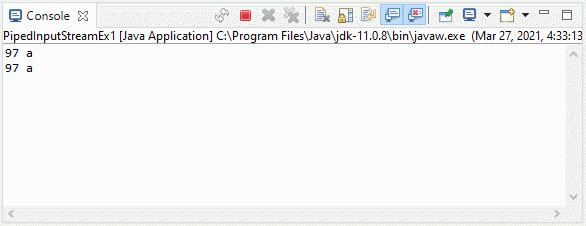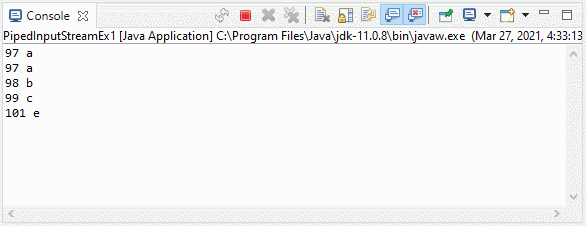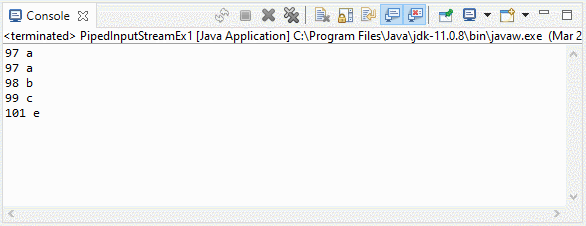
3. Example 2
Ví dụ: Sử dụng PipedInputStream, PipedOutputStream với BufferedInputStream và BufferedOutputStream để nâng cao hiệu xuất của chương trình.
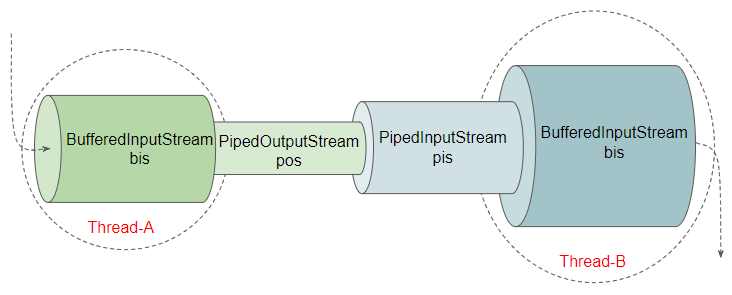
PipedInputStreamEx2.java
package org.o7planning.pipedinputstream.ex;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class PipedInputStreamEx2 {
private BufferedInputStream bufferedIS;
private BufferedOutputStream bufferedOS;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
new PipedInputStreamEx2().test();
}
private void test() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
pipedIS.connect(pipedOS);
this.bufferedIS = new BufferedInputStream(pipedIS);
this.bufferedOS = new BufferedOutputStream(pipedOS);
new ThreadB().start();
new ThreadA().start();
}
//
class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 'a', 97, 'b', 'c', 101 };
for (byte b : bytes) {
bufferedOS.write(b);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(bufferedOS);
}
}
}
//
class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int code;
while ((code = bufferedIS.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(code + " " + (char)code);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(bufferedIS);
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(InputStream in) {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(OutputStream out) {
if (out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}Các hướng dẫn Java IO
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java CharArrayWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FilterReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FilterWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PrintStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java StringReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java StringWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java LineNumberReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PushbackReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PrintWriter
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng luồng vào ra nhị phân trong Java
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng luồng vào ra ký tự trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ByteArrayOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PipedInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java OutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectOutputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PushbackInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java SequenceInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BufferedInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Reader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Writer
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java CharArrayReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ByteArrayInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java DataInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java ObjectInputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java InputStreamReader
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java OutputStreamWriter
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java InputStream
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java FileInputStream
Show More
- Hướng dẫn lập trình Java Servlet/JSP
- Các hướng dẫn Java New IO
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Cloud
- Các hướng dẫn Java Oracle ADF
- Các hướng dẫn Java Collections Framework
- Java cơ bản
- Các hướng dẫn Java Date Time
- Các thư viện mã nguồn mở Java
- Các hướng dẫn Java Web Services
- Các hướng dẫn Struts2 Framework
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Boot
