Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BiFunction
1. BiFunction
Trong Java 8, BiFunction là một functional interface, nó đại diện cho một toán tử chấp nhận hai giá trị đầu vào và trả về một giá trị.
Mã nguồn của interface BiFunction:
BiFunction
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BiFunction<T, U, R> {
R apply(T t, U u);
default <V> BiFunction<T, U, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t, U u) -> after.apply(apply(t, u));
}
}Xem thêm: Function là một functional interrface tương tự BiFunction, nhưng nó chấp nhận một tham số đầu vào và trả về một giá trị.
Ví dụ: Tạo một BiFunction chấp nhận 2 tham số đầu vào kiểu String và trả về kiểu String.
BiFunctionEx1.java
package org.o7planning.bifunction.ex;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
public class BiFunctionEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a BiFunction object directly.
// Accepts 2 input parameters of type String and return a String.
BiFunction<String, String, String> namer //
= (firstName, lastName) -> firstName + " " + lastName;
String fullName = namer.apply("James", "Smith");
System.out.println(fullName);
}
}Output:
James SmithDưới đây là danh sách các phương thức trong package java.util sử dụng BiFunction:
V | HashMap.compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | Hashtable.compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
default V | Map.compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | TreeMap.compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | HashMap.computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | Hashtable.computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
default V | Map.computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | TreeMap.computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | HashMap.merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | Hashtable.merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
default V | Map.merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
V | TreeMap.merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) |
default void | Map.replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) |
Ví dụ: Một đối tượng Map chứa các ánh xạ giữa tên quốc gia và chi phí thuê một căn hộ trong một tháng. Chúng ta sẽ cập nhập giá tăng 10% ngoại trừ Việt Nam.
BiFunctionEx2.java
package org.o7planning.bifunction.ex;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
public class BiFunctionEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Data in 2021.
// String country --> Float price to rent an apartment per month ($).
Map<String, Float> pricingMap = new HashMap<String, Float>();
pricingMap.put("Singapore", 2147f);
pricingMap.put("Sweden", 890f);
pricingMap.put("Japan", 770f);
pricingMap.put("Mexico", 345f);
pricingMap.put("Vietnam", 305f);
pricingMap.put("India", 156f);
// Pricing Map
System.out.println(pricingMap);
System.out.println();
// (String,Float) --> Float.
BiFunction<String, Float, Float> biFunction = (country, price) -> {
if (country.equals("Vietnam")) {
return price;
}
return price * 1.1f;
};
pricingMap.replaceAll(biFunction);
// After replacement.
System.out.println("After replacement:\n");
System.out.println(pricingMap);
}
}Output:
{Sweden=890.0, Vietnam=305.0, Singapore=2147.0, Japan=770.0, Mexico=345.0, India=156.0}
After replacement:
{Sweden=979.0, Vietnam=305.0, Singapore=2361.7, Japan=847.0, Mexico=379.5, India=171.6}2. andThen(Function after)
Phương thức andThen(after) trả về một BiFunction kết hợp. Đầu tiên, BiFunction.apply được gọi để biến (T,U) thành (R), sau đó after.apply được gọi để biến (R) thành (V). Nếu lỗi xẩy ra tại một trong 2 bước trên lỗi sẽ được chuyển tới người gọi (caller). Nếu lỗi xẩy ra tại BiFunction hiện tại thì after bị bỏ qua.
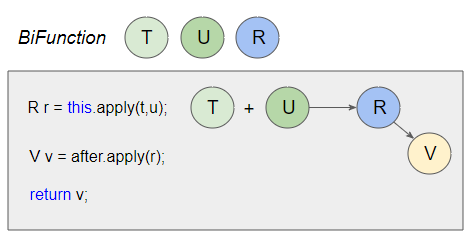
Mã nguồn của phương thức andThen(after) có thể hơi khó hiểu một chút:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BiFunction<T, U, R> {
R apply(T t, U u);
default <V> BiFunction<T, U, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t, U u) -> after.apply(apply(t, u));
}
}Và chúng ta có thể diễn giải mã nguồn trên một cách đơn giản hơn:
BiFunction (Simpler)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BiFunction<T, U, R> {
// (T,U) -> R
R apply(T t, U u);
// (T,U) -> V
default <V> BiFunction<T, U, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
BiFunction<T, U, V> ret = (T t, U u) -> {
// (T,U) -> R
R r = this.apply(t, u);
// R -> V
V v = after.apply(r);
return v;
};
return ret;
}
}Ví dụ:
BiFunction_andThen_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.bifunction.ex;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class BiFunction_andThen_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// BiFunction: (char,int) --> (String)
// Example: ('0', 3) --> "000"
BiFunction<Character, Integer, String> bif = (ch, n) -> {
String s="";
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) {
s+=ch;
}
return s;
};
// Function: (String) --> (String)
// Example: "abc" --> "ABC".
Function<String,String> after = s -> s.toUpperCase();
// Test:
String result = bif.andThen(after).apply('a', 3);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
}
}Output:
Result: AAA3. BiFunction + Method reference
Nếu một phương thức có hai tham số và trả về một giá trị, thì tham chiếu của nó có thể coi như là một BiFunction.
Ví dụ: Phương thức tĩnh Math.max(int,int) chấp nhận 2 tham số và trả về kiểu Integer, vậy tham chiếu của nó là Math::max có thể coi là một BiFunction.
BiFunction_mRef_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.bifunction.ex;
public class BiFunction_mRef_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a BiFunction from method reference.
// (Integer,Integer) --> (Integer)
BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer> biFunc = Math::max;
int max = biFunc.apply(10, 20); // 20
System.out.println("Max: " + max); // 20
}
}Output:
Max: 20Ví dụ: BiFunction + non-static method reference:
BiFunction_mRef_ex2.java
package org.o7planning.bifunction.ex;
public class BiFunction_mRef_ex2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CardTemplate template = new CardTemplate("Designed by Tom");
// Create a BiFunction from method reference.
// (String,String) --> (String)
BiFunction<String, String, String> biFunc = template::getContent;
String cardContent = biFunc.apply("Eli", "Smith");
System.out.println(cardContent);
}
}
class CardTemplate {
private String someInfo;
public CardTemplate(String someInfo) {
this.someInfo = someInfo;
}
public String getContent(String firstName, String lastName) {
return "----- ~~~~~ -----\n" //
+ "First name: " + firstName + "\n" //
+ "Last name: " + lastName + "\n" //
+ this.someInfo;
}
}Output:
----- ~~~~~ -----
First name: Eli
Last name: Smith
Designed by Tom4. BiFunction + Constructor reference
Như chúng ta đã biết, constructor là một phương thức đặc biệt trả về một đối tượng. Vì vậy, nếu một constructor có 2 tham số thì tham chiếu của nó sẽ được coi là một BiFunction.
BiFunction_cRef_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.bifunction.ex;
public class BiFunction_cRef_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a BiFunction from constructor reference.
// (String,Integer) --> (Staff)
BiFunction<String, Integer, Staff> biFunc = Staff::new;
Staff tom = biFunc.apply("Tom", 1000);
Staff jerry = biFunc.apply("Jerry", 2000);
tom.showInfo();
jerry.showInfo();
}
public static class Staff {
private String fullName;
private int salary;
public Staff(String fullName,int salary) {
this.fullName= fullName;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void showInfo() {
System.out.println("Full Name: " + this.fullName +", Salary: " + this.salary);
}
}
}Output:
Full Name: Tom, Salary: 1000
Full Name: Jerry, Salary: 2000Java cơ bản
- Tùy biến trình biên dịch java xử lý Annotation của bạn (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Lập trình Java theo nhóm sử dụng Eclipse và SVN
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java WeakReference
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java PhantomReference
- Hướng dẫn nén và giải nén trong Java
- Cấu hình Eclipse để sử dụng JDK thay vì JRE
- Phương thức String.format() và printf() trong Java
- Cú pháp và các tính năng mới trong Java 5
- Cú pháp và các tính năng mới trong Java 8
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng biểu thức chính quy trong Java
- Hướng dẫn lập trình đa luồng trong Java - Java Multithreading
- Thư viện điều khiển các loại cơ sở dữ liệu khác nhau trong Java
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng Java JDBC kết nối cơ sở dữ liệu
- Lấy các giá trị của các cột tự động tăng khi Insert một bản ghi sử dụng JDBC
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Stream
- Functional Interface trong Java
- Giới thiệu về Raspberry Pi
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Predicate
- Abstract class và Interface trong Java
- Access modifier trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Enum
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Annotation
- So sánh và sắp xếp trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java String, StringBuffer và StringBuilder
- Hướng dẫn xử lý ngoại lệ trong Java - Java Exception Handling
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Generics
- Thao tác với tập tin và thư mục trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BiPredicate
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Consumer
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BiConsumer
- Bắt đầu với Java cần những gì?
- Lịch sử của Java và sự khác biệt giữa Oracle JDK và OpenJDK
- Cài đặt Java trên Windows
- Cài đặt Java trên Ubuntu
- Cài đặt OpenJDK trên Ubuntu
- Cài đặt Eclipse
- Cài đặt Eclipse trên Ubuntu
- Học nhanh Java cho người mới bắt đầu
- Lịch sử của bit và byte trong khoa học máy tính
- Các kiểu dữ liệu trong Java
- Các toán tử Bitwise
- Câu lệnh rẽ nhánh (if else) trong Java
- Câu lệnh rẽ nhánh switch trong Java
- Vòng lặp trong Java
- Mảng (Array) trong Java
- JDK Javadoc định dạng CHM
- Thừa kế và đa hình trong Java
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Function
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java BiFunction
- Ví dụ về Java encoding và decoding sử dụng Apache Base64
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Reflection
- Hướng dẫn gọi phương thức từ xa với Java RMI
- Hướng dẫn lập trình Java Socket
- Các nền tảng nào bạn nên chọn để lập trình ứng dụng Java Desktop?
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Commons IO
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Commons Email
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Commons Logging
- Tìm hiểu về Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode và Object.equals
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java SoftReference
- Hướng dẫn và ví dụ Java Supplier
- Lập trình Java hướng khía cạnh với AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Hướng dẫn lập trình Java Servlet/JSP
- Các hướng dẫn Java Collections Framework
- Java API cho HTML & XML
- Các hướng dẫn Java IO
- Các hướng dẫn Java Date Time
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Boot
- Các hướng dẫn Maven
- Các hướng dẫn Gradle
- Các hướng dẫn Java Web Services
- Các hướng dẫn lập trình Java SWT
- Các hướng dẫn lập trình JavaFX
- Các hướng dẫn Java Oracle ADF
- Các hướng dẫn Struts2 Framework
- Các hướng dẫn Spring Cloud
